The Russian education system has a rich history, dating back to the medieval period. Over centuries, it has evolved significantly, reflecting the nation’s political, social, and economic changes. Today, it stands as a complex and multifaceted system, shaping the future of a vast country.
Historical Roots
- Medieval Period: Early education in Russia was primarily religious, centered around monasteries and churches. The Cyrillic alphabet, developed by Cyril and Methodius, was instrumental in spreading literacy.
- Imperial Russia: Under the Tsars, education became more formalized. The establishment of universities and secondary schools, particularly in major cities, expanded access to higher education.
- Soviet Era: The Soviet Union placed a strong emphasis on education, aiming to create a highly skilled workforce. The system was centralized, with a focus on STEM subjects and ideological indoctrination.
- Post-Soviet Era: Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia’s education system underwent significant reforms. While it retained some elements of the Soviet model, it also embraced market-oriented principles and international standards.
Modern Russian Education
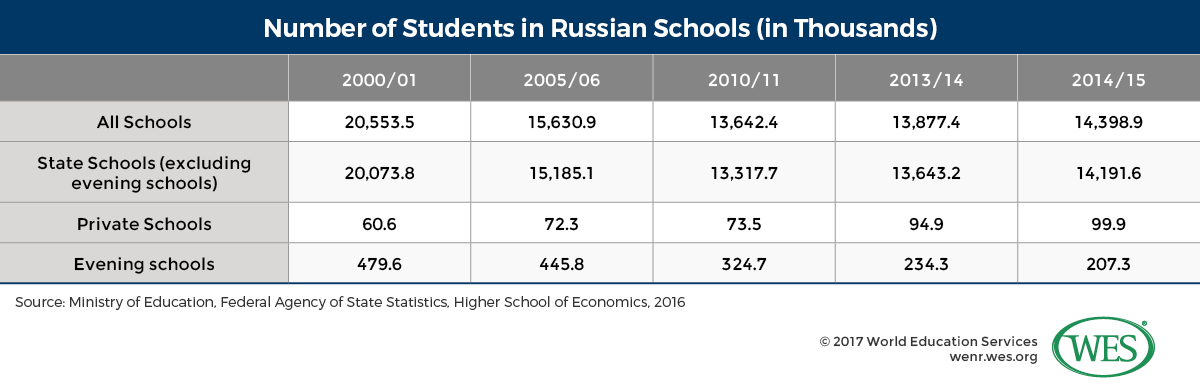
Today, Russia’s education system is a diverse and dynamic landscape. It comprises:
- Primary Education: Compulsory for children aged 6-7 to 15-16.
- Secondary Education: Divided into basic and advanced levels, preparing students for higher education or vocational training.
- Higher Education: Offers a wide range of programs, including bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees.
Key Features of the Modern Russian Education System:
- Strong Emphasis on STEM: Mathematics, science, and technology remain core subjects, reflecting the country’s industrial and technological aspirations.
- Language Learning: Foreign language study, particularly English, is increasingly important.
- Vocational Education: A strong emphasis on vocational training to meet the needs of the labor market.
- Internationalization: Russian universities are actively seeking international partnerships and attracting foreign students.
- Challenges and Reforms: The system faces challenges such as outdated infrastructure, uneven quality, and bureaucratic hurdles. Reforms are ongoing to address these issues and improve the overall quality of education.
Notable Russian Universities:
- Moscow State University (MSU): One of the world’s leading universities, offering a wide range of programs.
- Saint Petersburg State University (SPbSU): A prestigious institution with a strong focus on the humanities and social sciences.
- Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT): A renowned technical university specializing in physics, mathematics, and computer science.
Russian education has a rich history and continues to evolve. As the country strives to become a global leader in science, technology, and innovation, its education system plays a crucial role in shaping the future of Russia and its people.






Leave a Reply