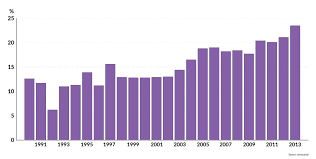
Russia’s import landscape is a complex interplay of domestic demand, geopolitical factors, and economic policies. While the country is known for its vast natural resources and export-oriented industries, it also relies on imports to meet various domestic needs.
Key Import Categories
- Machinery and Equipment: Russia imports advanced machinery and equipment, particularly for its industrial sector. This includes machinery for manufacturing, mining, and agriculture.
- Consumer Goods: A wide range of consumer goods, such as electronics, automobiles, and clothing, are imported to meet domestic demand.
- Food Products: Russia imports food products, including fruits, vegetables, and meat, to supplement domestic production.
- Pharmaceuticals: Russia imports pharmaceuticals to meet the country’s healthcare needs.
Major Import Sources
- European Union: The EU remains a significant source of imports for Russia, particularly high-tech products and consumer goods.
- China: China has emerged as a major supplier of consumer goods, machinery, and electronics to Russia.
- Other Countries: Russia also imports from countries in Asia, such as Japan and South Korea, as well as from the United States.
Challenges and Opportunities
Russia’s imports are subject to various challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical tensions with Western countries can lead to trade restrictions and import bans.
- Currency Fluctuations: Fluctuations in the exchange rate can impact the cost of imports.
- Infrastructure Constraints: Inadequate infrastructure can hinder the efficient import and distribution of goods.
However, Russia also has opportunities to optimize its import strategy:
- Import Substitution: Promoting domestic production to reduce reliance on imports.
- Diversification of Suppliers: Reducing dependence on a limited number of suppliers to mitigate risks.
- Improving Logistics: Investing in infrastructure and logistics to streamline the import process.
- Technological Innovation: Encouraging technological innovation to develop domestic alternatives to imported goods.
By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on opportunities, Russia can optimize its import strategy and contribute to the sustainable development of its economy.






Leave a Reply