Russia’s international relations are characterized by a complex mix of cooperation and confrontation, shaped by its historical legacy, geopolitical ambitions, and economic interests. As a major global power, Russia seeks to reassert its influence on the world stage, often challenging the established Western-led order.
Key Foreign Policy Goals
- Great Power Status: Russia aims to reestablish itself as a global superpower, capable of shaping international affairs and defending its national interests.
- Buffer Zone: Russia seeks to maintain a buffer zone of friendly states around its borders, particularly in the former Soviet republics.
- Energy Dominance: Leveraging its vast energy resources, Russia aims to influence global energy markets and secure geopolitical leverage.
- Countering Western Influence: Russia seeks to counterbalance Western influence, particularly in its near abroad and regions of strategic importance.
Major Challenges and Opportunities
Russia faces several significant challenges in its international relations:
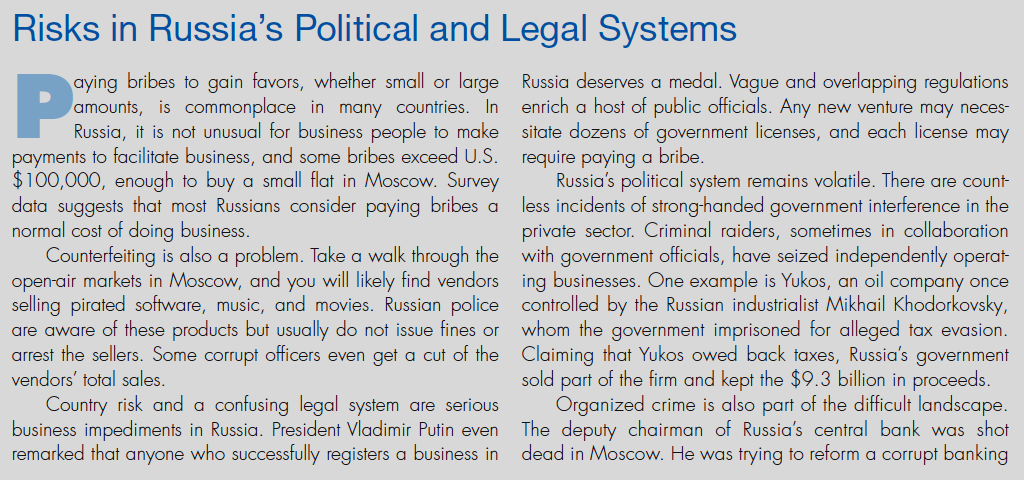
- Western Sanctions: Economic sanctions imposed by Western countries have hindered Russia’s economic development and limited its access to international financial markets.
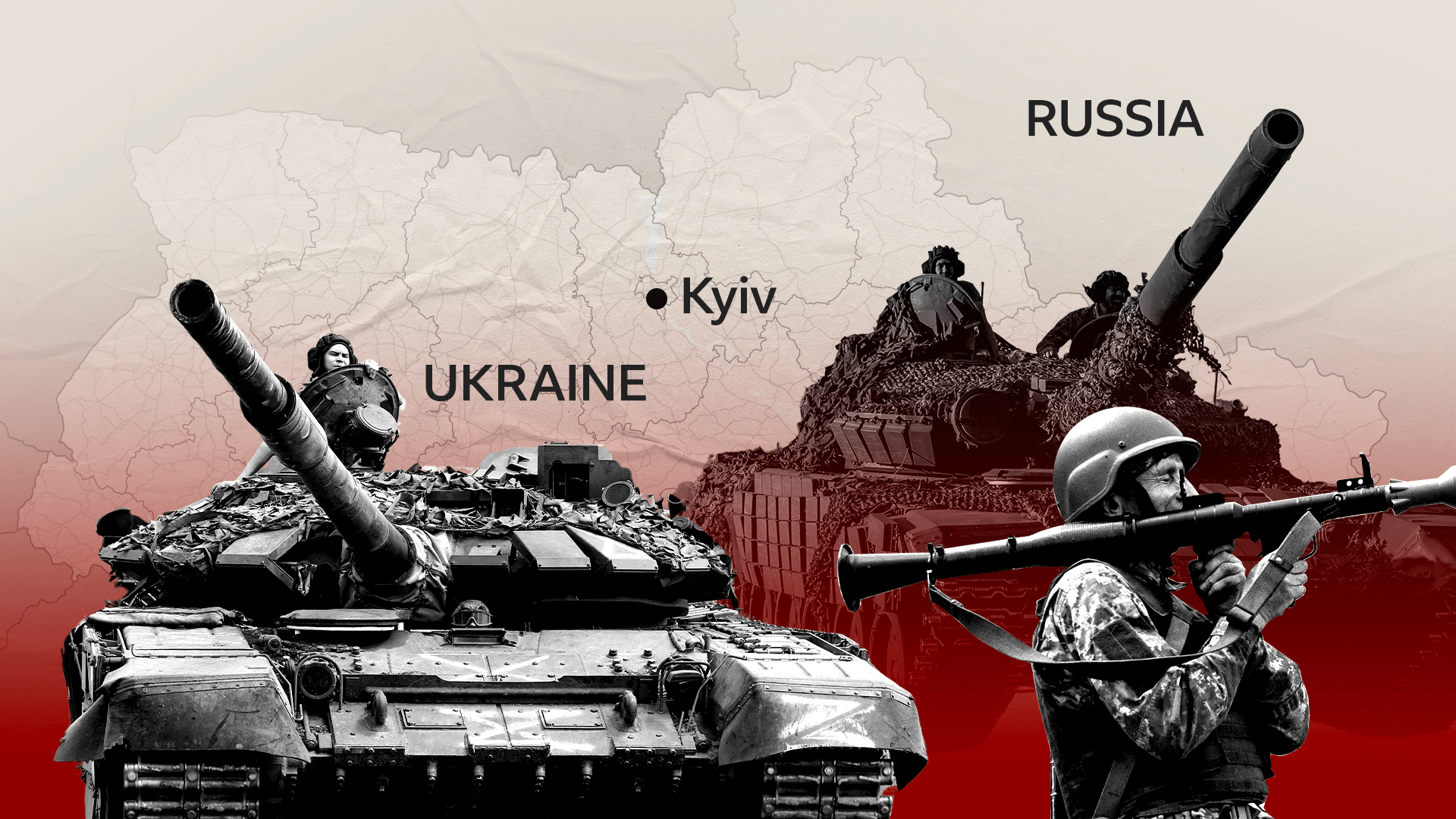
- NATO Expansion: The eastward expansion of NATO has been a major source of tension between Russia and the West.
- Geopolitical Competition: Increasing competition from emerging powers like China has added to Russia’s geopolitical challenges.
- Domestic Challenges: Economic stagnation, corruption, and demographic decline pose significant challenges to Russia’s long-term stability.
However, Russia also has several opportunities to strengthen its international position:
- Energy Resources: Russia’s vast energy resources give it significant geopolitical leverage.
- Military Power: Russia maintains a powerful military, including nuclear weapons, which can be used to deter potential adversaries and project power.
- Diplomatic Influence: Russia can use diplomacy to build alliances, negotiate agreements, and shape international discourse.
- Economic Diversification: By diversifying its economy and reducing its reliance on energy exports, Russia can improve its economic resilience and reduce its vulnerability to external shocks.
Key Partnerships and Alliances
- China: Russia and China have developed a strategic partnership, based on shared interests and mutual benefit.
- India: Russia and India have a long-standing relationship, characterized by strategic cooperation in various fields.
- Belarus: Russia and Belarus have a close alliance, with Belarus often acting as a buffer state between Russia and the West.
- Other Post-Soviet States: Russia maintains close ties with several former Soviet republics, particularly those in Central Asia.
The future of Russia’s international relations will depend on a variety of factors, including domestic political developments, global economic trends, and geopolitical shifts. As Russia navigates the complexities of the 21st century, its foreign policy will continue to shape the global landscape.







Leave a Reply