In recent years, Russia has implemented a series of export controls in response to geopolitical tensions and economic sanctions imposed by Western countries. These controls aim to protect critical technologies, strategic industries, and national security interests.
Key Drivers of Russian Export Controls
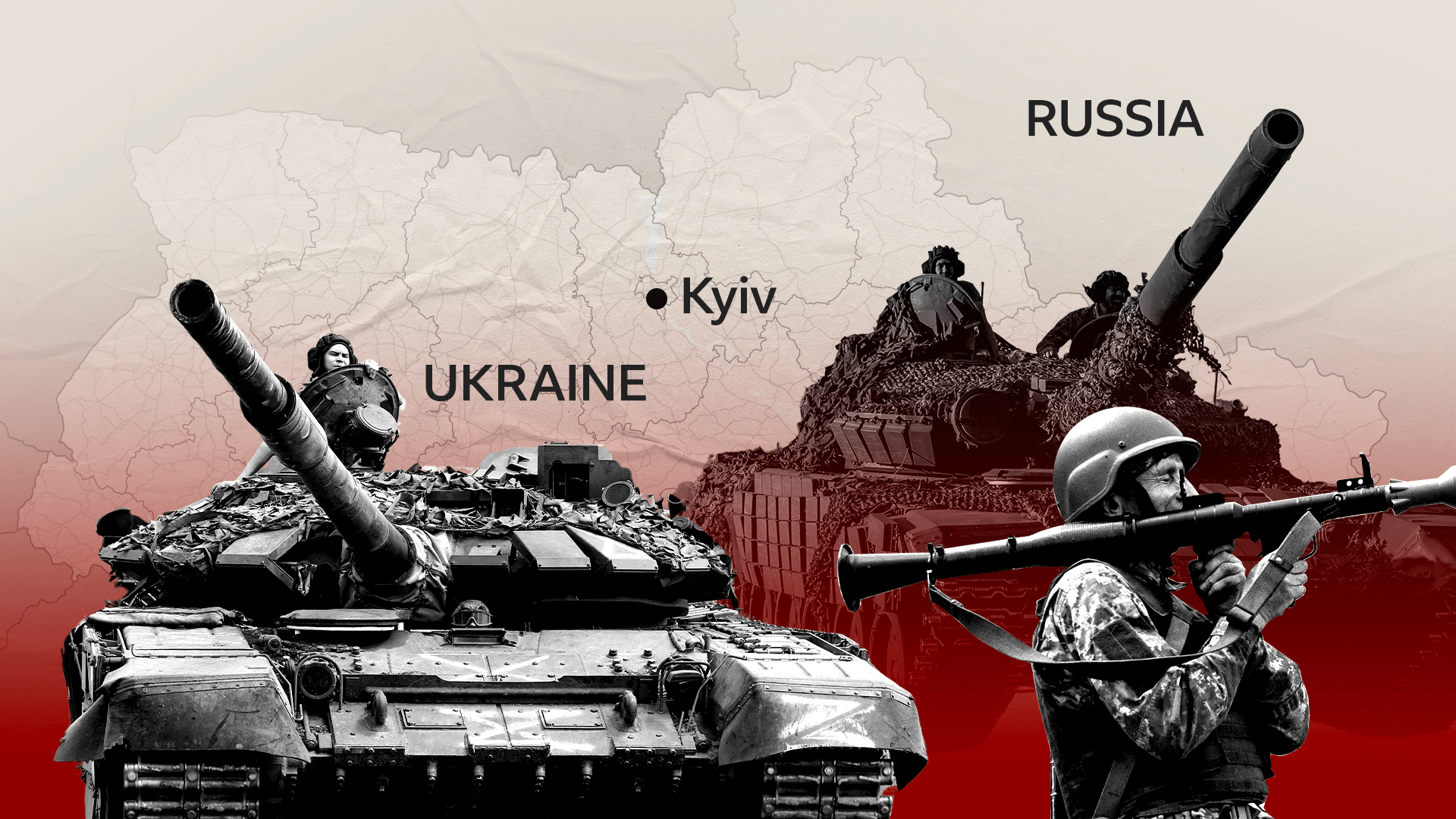
- Geopolitical Tensions: The deteriorating relationship between Russia and Western countries, particularly after the annexation of Crimea and the invasion of Ukraine, has led to increased geopolitical tensions and the imposition of sanctions.
- Technological Sovereignty: Russia seeks to develop its own technological capabilities and reduce reliance on foreign technology, particularly in strategic sectors such as defense, aerospace, and nuclear energy.
- National Security: Export controls are used to prevent the proliferation of sensitive technologies and to protect national security interests.
Types of Export Controls Implemented by Russia
- Dual-Use Goods and Technologies: Russia has implemented strict controls on the export of dual-use goods and technologies, which can be used for both civilian and military purposes.
- Military and Strategic Goods: The export of military equipment and weapons is subject to strict licensing and regulatory requirements.
- Sensitive Technologies: Russia has imposed restrictions on the export of advanced technologies, such as semiconductors, telecommunications equipment, and artificial intelligence.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Russia has tightened intellectual property rights protection to prevent the unauthorized export of technology and know-how.
Impact of Export Controls on the Global Economy
Russia’s export controls have had a significant impact on the global economy, particularly in the technology and defense sectors. These controls can disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and limit access to critical technologies. Additionally, they can lead to retaliatory measures from other countries, further escalating geopolitical tensions.
Future Outlook
As the geopolitical landscape continues to evolve, Russia is likely to maintain a cautious approach to export controls. The country will need to balance its desire to protect its strategic interests with the need to attract foreign investment and integrate into the global economy.
To mitigate the negative impacts of export controls, Russia may consider:
- Diversifying Trade Partners: Expanding trade relations with countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America to reduce reliance on Western markets.
- Promoting Domestic Production: Investing in domestic research and development to reduce dependence on foreign technology.
- Liberalizing Economic Policies: Implementing reforms to create a more attractive business environment and encourage foreign investment.
By carefully navigating the complex geopolitical landscape and implementing effective economic policies, Russia can mitigate the negative impacts of export controls and ensure its long-term economic and technological development.







Leave a Reply