Great power status is a complex and contested concept that has evolved over time. Historically, great powers have been characterized by their military, economic, and political influence on a global scale. However, in the 21st century, the definition of a great power has become more nuanced, reflecting the changing dynamics of international relations.
Key Attributes of a Great Power
While the specific criteria for great power status may vary, several key attributes are commonly associated with this designation:
- Military Power: A great power possesses a strong military capable of projecting power globally. This includes a large and technologically advanced military, nuclear weapons, and a robust defense industry.
- Economic Power: A great power has a strong economy with a diverse industrial base and significant global trade. It can influence global markets and financial systems.
- Political Influence: A great power wields significant political influence, shaping international norms and institutions. It can mobilize international support for its policies and exert diplomatic pressure on other states.
- Cultural Influence: A great power often has a rich culture and history, and its language, arts, and ideas are influential globally.
The Rise and Fall of Great Powers
Throughout history, various states have risen and fallen as great powers. The Roman Empire, the British Empire, and the United States are examples of historical great powers. The rise and fall of great powers is often influenced by a combination of factors, including economic, technological, and political developments.
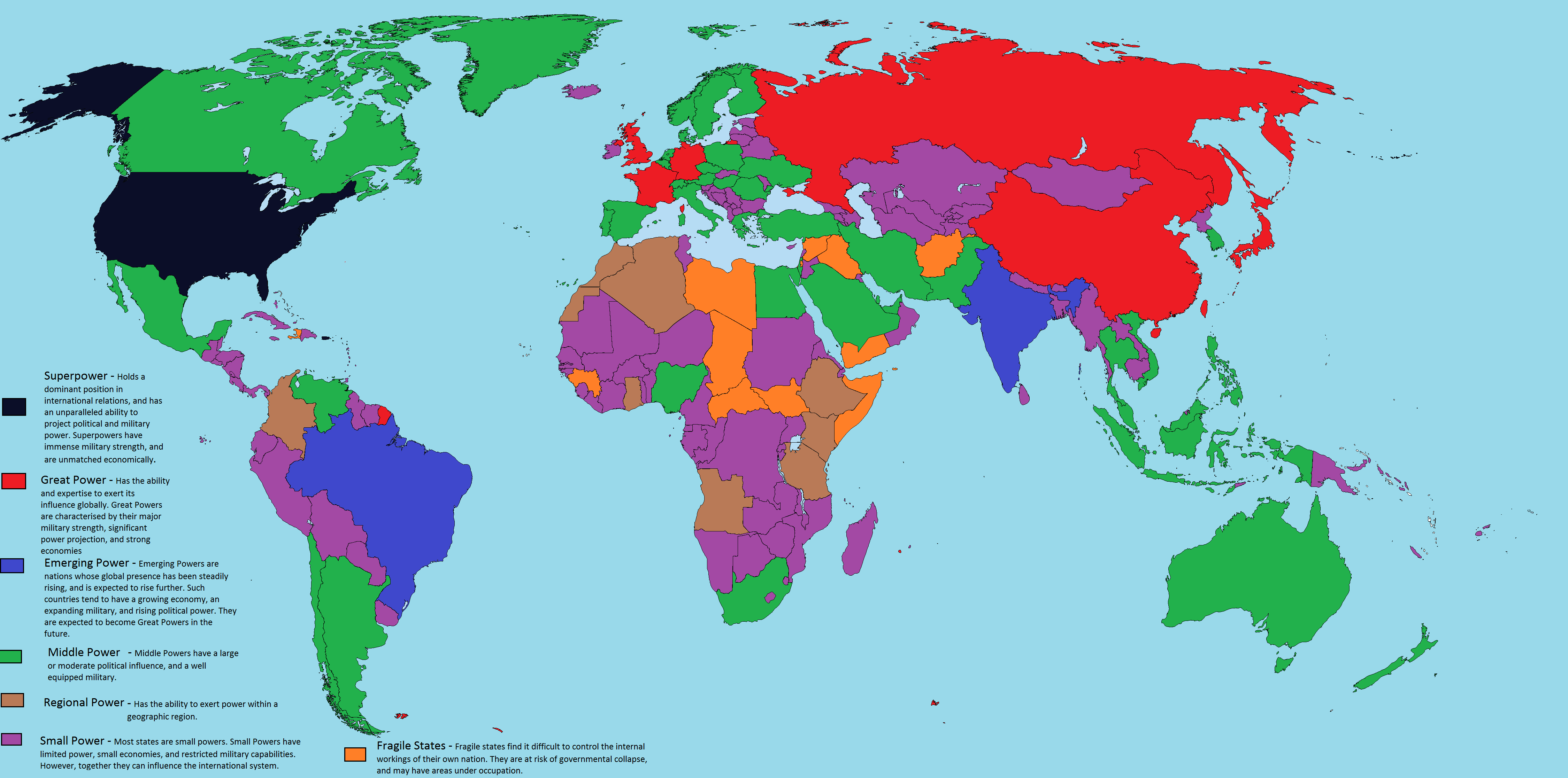
Great Powers in the 21st Century
In the 21st century, the traditional concept of great power status is being challenged by the rise of new powers and the changing nature of international relations. While the United States remains the dominant global power, other states, such as China and Russia, are vying for greater influence.
- The United States: The United States remains the world’s only superpower, with a formidable military, a strong economy, and significant cultural influence. However, the country faces challenges, including rising debt, political polarization, and the rise of China.
- China: China has emerged as a major global power, driven by rapid economic growth and a growing military. China seeks to shape the international order and challenge US dominance.
- Russia: Russia, despite its economic and demographic challenges, remains a nuclear power with significant military capabilities. It seeks to reassert itself as a global power and influence regional affairs.
The Future of Great Power Competition
The future of great power competition is uncertain. The rise of new powers, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts are all shaping the global landscape. As the balance of power shifts, the world may witness increased competition, cooperation, and conflict among great powers.
The concept of great power status is likely to continue to evolve in the 21st century. As the world becomes more interconnected and complex, the traditional attributes of great power status may not be sufficient to define the leading powers of the future. New factors, such as technological innovation, cybersecurity, and climate change, may play a crucial role in shaping the global order.






Leave a Reply