While Russia has historically been a major global power, its current global leadership role is complex and multifaceted. It’s a blend of traditional great power ambitions, geopolitical maneuvering, and economic realities.
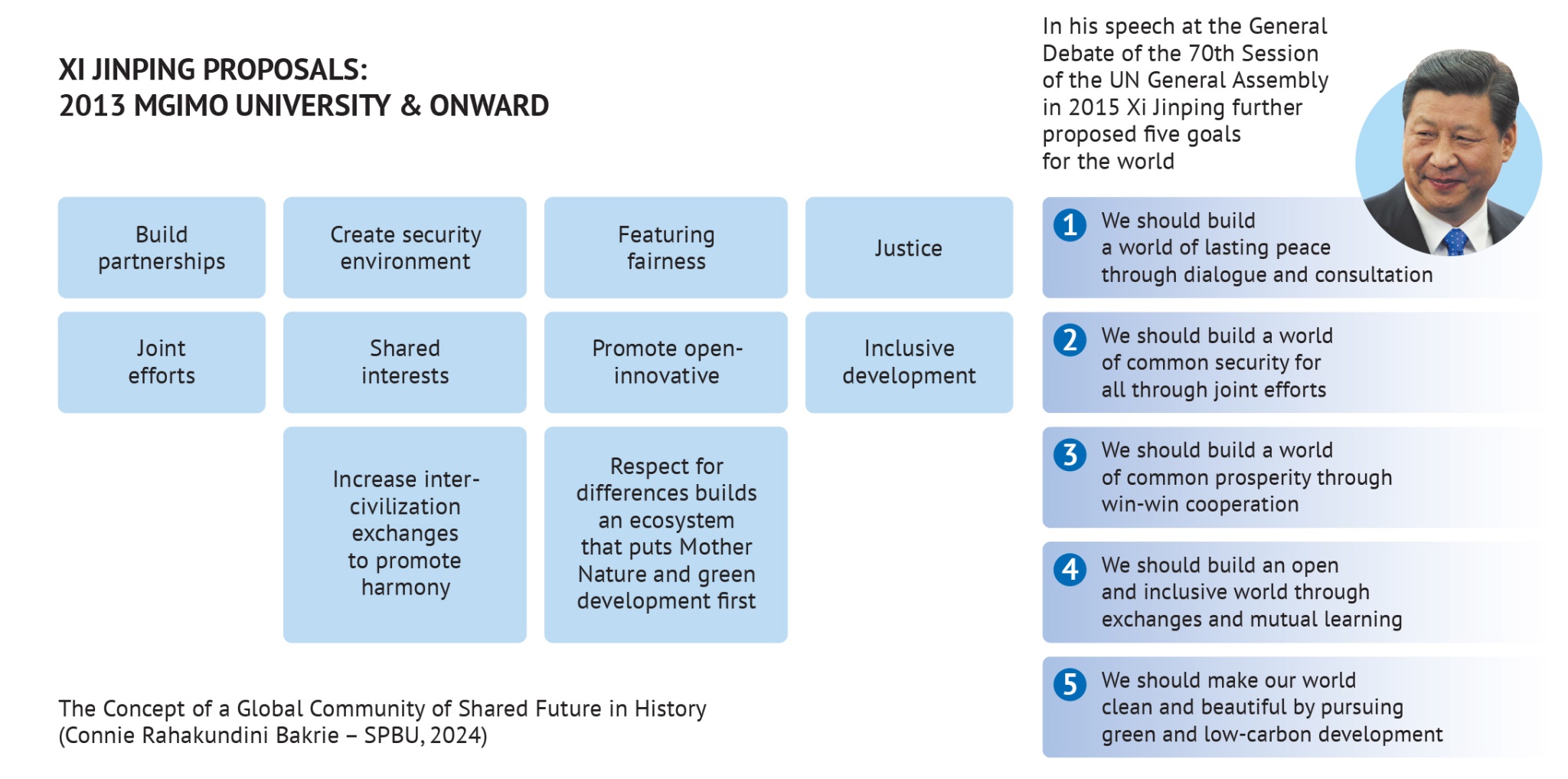
Key Factors Shaping Russia’s Global Leadership
- Energy Resources: Russia possesses vast reserves of natural gas and oil, making it a major energy supplier to Europe and other regions. This energy leverage allows Russia to exert geopolitical influence.
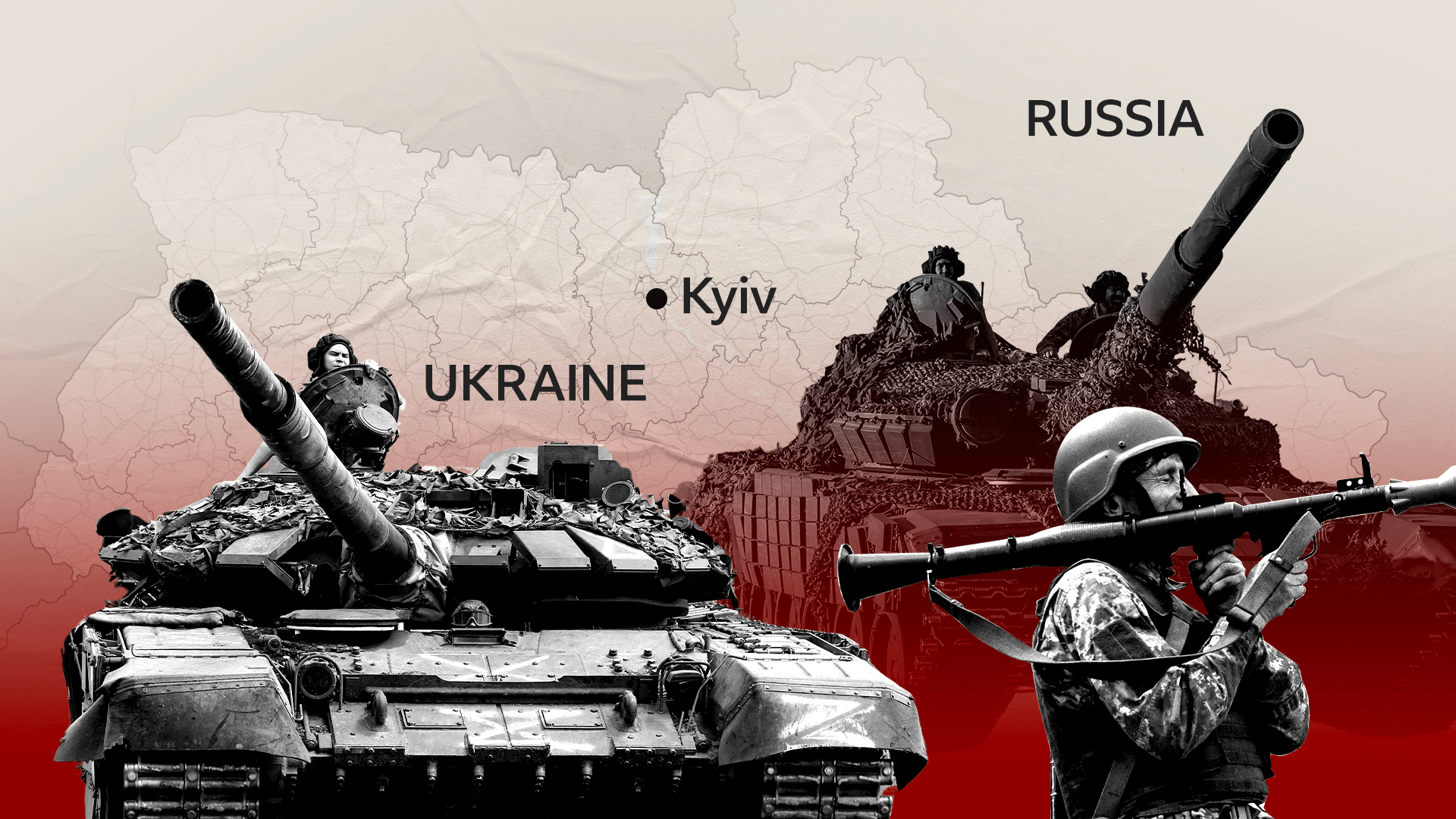
- Military Power: Russia maintains a formidable military, including a significant nuclear arsenal. This military strength enables it to project power globally and assert its interests in regional conflicts.
- Geopolitical Ambitions: Russia seeks to restore its influence in its traditional sphere of influence, particularly in the former Soviet republics. This ambition has led to tensions with Western powers and neighboring countries.
- Nationalism and Patriotism: A resurgence of nationalism and patriotism has fueled Russia’s assertive foreign policy. This sentiment has been used to mobilize public support for the government’s actions.
Areas of Russian Influence
- Europe: Russia has significant influence over European countries, particularly through energy exports and geopolitical maneuvering.
- Middle East: Russia has played a key role in regional conflicts, such as the Syrian Civil War, and has sought to expand its influence in the region.
- Asia-Pacific: Russia has strengthened its ties with Asian countries, particularly China, to counterbalance Western influence and secure its economic interests.
- Africa: Russia has increased its engagement with African countries, offering economic and military assistance.
- Latin America: Russia has sought to expand its influence in Latin America, particularly through diplomatic and economic ties.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its global ambitions, Russia faces several challenges:
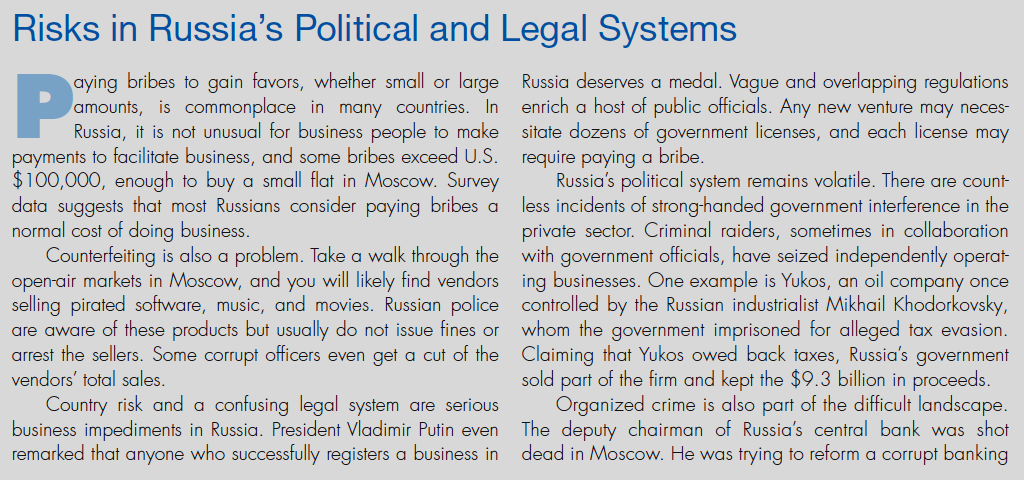
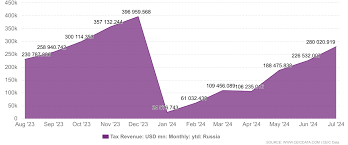
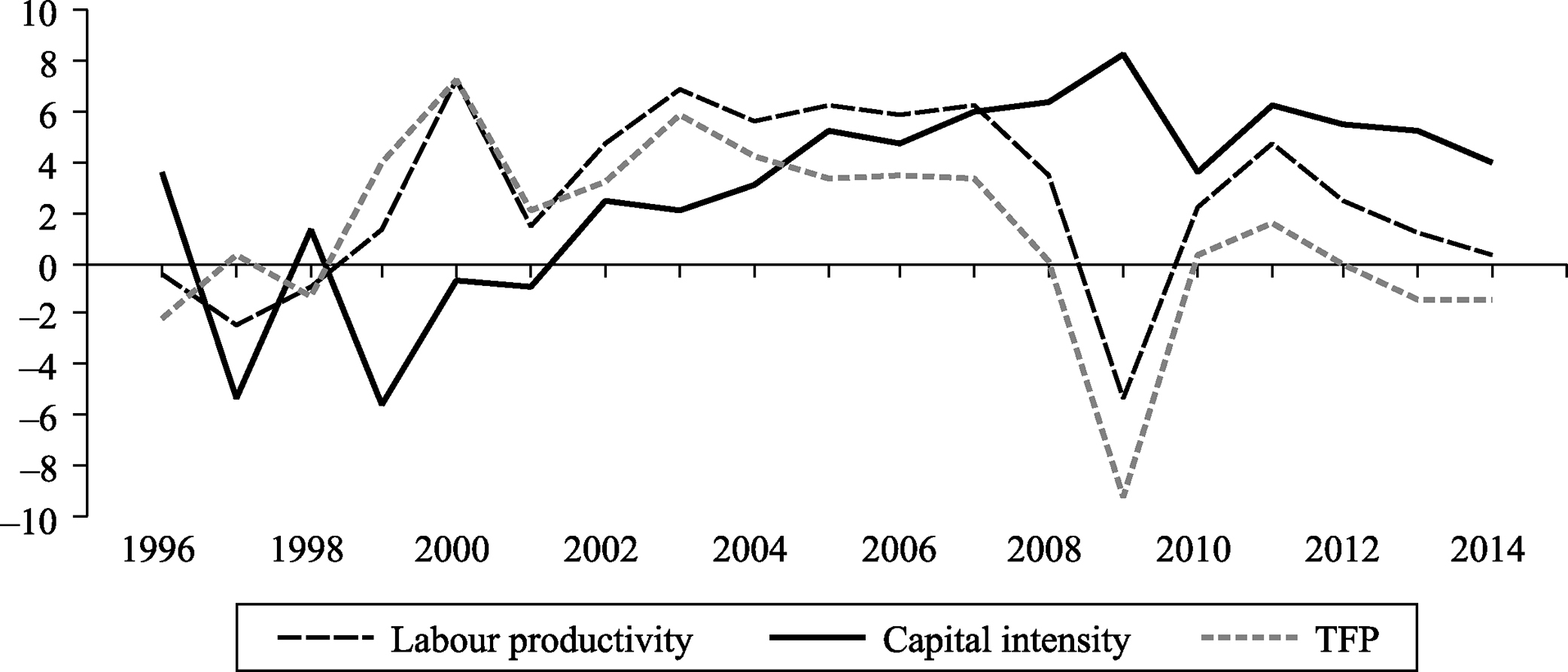
- Economic Stagnation: Russia’s economy is heavily reliant on energy exports, making it vulnerable to global price fluctuations and Western sanctions.
- Demographic Decline: Russia’s population is aging and shrinking, posing long-term challenges to its economic and military power.
- International Isolation: Russia’s aggressive foreign policy has led to increased international isolation and sanctions, hindering its economic development and diplomatic efforts.
- Domestic Dissent: Growing domestic discontent and political repression could undermine the stability of the Russian regime and its foreign policy objectives.
The Future of Russia’s Global Leadership
The future of Russia’s global leadership is uncertain. While Russia may continue to pursue an assertive and confrontational approach, it is also likely to adapt to changing global dynamics and domestic constraints. Key factors that will shape Russia’s future trajectory include:
- The evolution of the Russia-China relationship: The deepening strategic partnership between the two powers could reshape the global balance of power.
- The impact of Western sanctions and diplomatic pressure: Continued sanctions and diplomatic isolation could further weaken the Russian economy and limit its foreign policy options.
- Domestic political developments in Russia: Any significant political change in Russia could have far-reaching implications for its foreign policy.
As Russia navigates the complexities of the 21st century, its impact on the global stage will continue to be significant. However, its ability to achieve its global ambitions will depend on its capacity to address domestic challenges, manage geopolitical tensions, and adapt to a rapidly changing world.






Leave a Reply